Thyroid Care in India: Understanding Symptoms, Treatment, and Costs.
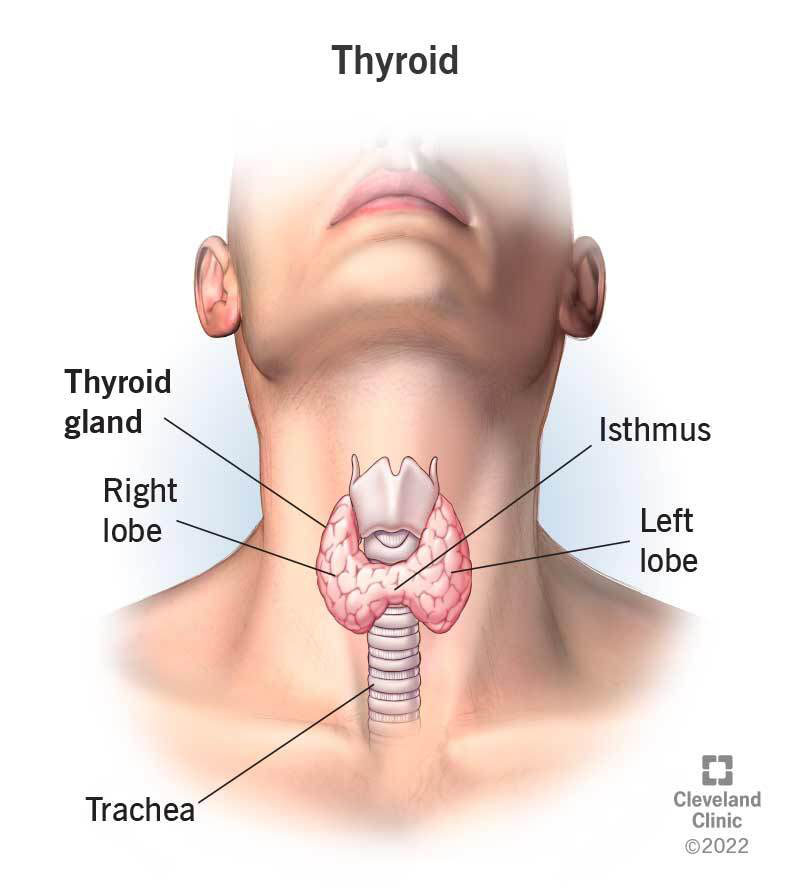
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of your neck, just below the Adam’s apple. It plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions by producing hormones, primarily:
- Thyroxine (T4): The primary hormone produced, it influences metabolism, growth, and development.
- Triiodothyronine (T3): More active than T4, it regulates metabolism and energy levels.
- Calcitonin: Helps regulate calcium levels in the blood.
Functions of the Thyroid
- Metabolism: Controls how your body uses energy.
- Growth and Development: Essential for normal growth in children.
- Body Temperature: Helps maintain a stable body temperature.
- Heart Rate: Influences heart function and blood circulation.
Common Disorders
- Hypothyroidism: An underactive thyroid that leads to fatigue, weight gain, and depression.
- Hyperthyroidism: An overactive thyroid that can cause weight loss, increased heart rate, and anxiety.
- Goiter: Enlargement of the thyroid, which can occur in both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
- Thyroid Nodules: Lumps in the thyroid that can be benign or, in some cases, cancerous.
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks the thyroid, leading to hypothyroidism.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis often involves blood tests to measure hormone levels (like TSH, T3, and T4). Treatment varies depending on the condition and can include hormone replacement therapy, medications, or, in some cases, surgery.
various causes:
Hypothyroidism
- Autoimmune Disease: Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is the most common cause, where the immune system attacks the thyroid.
- Iodine Deficiency: Insufficient iodine intake can impair hormone production.
- Thyroid Surgery: Removal of all or part of the thyroid can lead to reduced hormone production.
- Radiation Therapy: Treatment for cancers in the neck can damage the thyroid.
- Medications: Certain drugs, such as lithium or amiodarone, can affect thyroid function.
Hyperthyroidism
- Graves’ Disease: An autoimmune disorder that causes the thyroid to produce excess hormones.
- Thyroid Nodules: Overactive nodules can produce too much hormone independently.
- Excessive Iodine Intake: Consuming too much iodine can trigger overproduction of hormones.
- Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid can lead to temporary hyperthyroidism.
Other Issues
- Thyroid Cancer: Abnormal growths in the thyroid may disrupt hormone production.
- Congenital Conditions: Some people are born with thyroid dysfunction.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
- Stress: Chronic stress can influence thyroid function.
- Diet: A diet lacking in essential nutrients (like selenium and zinc) may impact thyroid health.
Symptoms:
Hypothyroidism Symptoms
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and lack of energy.
- Weight Gain: Unexplained weight increase despite normal eating habits.
- Cold Intolerance: Increased sensitivity to cold temperatures.
- Dry Skin and Hair: Skin may become rough, and hair may become brittle and thin.
- Constipation: Slower digestive processes leading to infrequent bowel movements.
- Muscle Weakness: General weakness or aches in muscles.
- Depression: Feelings of sadness or low mood.
- Memory Problems: Difficulty concentrating or remembering things.
- Menstrual Changes: Irregularities in menstrual cycles.
Hyperthyroidism Symptoms
- Weight Loss: Unintended weight loss despite increased appetite.
- Increased Heart Rate: Palpitations or a rapid heartbeat.
- Nervousness or Anxiety: Heightened feelings of anxiety or irritability.
- Heat Intolerance: Increased sensitivity to heat and excessive sweating.
- Tremors: Slight shaking, often in the hands.
- Increased Appetite: A feeling of hunger more frequently.
- Menstrual Changes: Lighter or less frequent periods.
- Fatigue or Muscle Weakness: Especially in the upper arms and thighs.
- Goiter: An enlarged thyroid gland, which may appear as swelling at the base of the neck.
Other Symptoms
- Hair Changes: Thinning hair in hypothyroidism, while hyperthyroidism may cause fine, brittle hair.
- Sleep Disturbances: Insomnia or disrupted sleep patterns can occur in both conditions.
Treatment:
Hypothyroidism Treatment
- Hormone Replacement Therapy:
- Levothyroxine (T4): The most common treatment, usually taken in the form of a daily pill. Common brands include Thyronorm and Eltroxin.
- Regular Monitoring: Patients require regular blood tests to monitor TSH levels and adjust dosages accordingly.
- Diet and Lifestyle:
- Iodine: Ensuring adequate iodine intake, which may include iodized salt or iodine-rich foods.
- Regular Exercise: Helps in managing weight and improving energy levels.
Hyperthyroidism Treatment
- Antithyroid Medications:
- Methimazole or Carbimazole: These medications reduce hormone production.
- Beta-blockers: May be prescribed to control symptoms like rapid heart rate and anxiety.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy:
- This treatment helps to destroy overactive thyroid cells. It’s often a preferred option for Graves’ disease.
- Surgery:
- In cases where medication and radioactive iodine are not effective or suitable, partial or total thyroidectomy may be performed.
Regular Monitoring
- Blood Tests: Regular follow-ups to monitor hormone levels are essential for both conditions.
Lifestyle and Dietary Recommendations
- Balanced Diet: Including selenium, zinc, and vitamins that support thyroid health.
- Avoid Goitrogens: Foods like soy and cruciferous vegetables should be consumed in moderation, especially raw, as they can interfere with thyroid function.
Alternative Therapies
- Some people explore Ayurvedic treatments or herbal supplements. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider before starting any alternative therapies.
Accessing Treatment
- Healthcare Facilities: Major cities have specialized endocrine clinics, and many hospitals offer thyroid testing and treatment.
- Specialists: Endocrinologists or general practitioners can provide diagnosis and treatment plans.
Diagnosis:
Clinical Evaluation
- Medical History: Discussion of symptoms, family history of thyroid disease, and any prior thyroid issues.
- Physical Examination: Checking for signs like goiter, changes in skin or hair, and symptoms related to hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
Blood Tests
- TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone):
- The most common initial test. High levels suggest hypothyroidism, while low levels indicate hyperthyroidism.
- Free T4 (Thyroxine):
- Measures the level of thyroxine in the blood. Helps confirm hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
- Free T3 (Triiodothyronine):
- Often measured in conjunction with TSH and T4, especially if hyperthyroidism is suspected.
- Thyroid Antibodies:
- Anti-TPO (Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies): High levels can indicate Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- TSI (Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobulin): May be tested for Graves’ disease.
- Thyroid Function Tests:
- A comprehensive panel may include all the above tests to provide a full picture of thyroid health.
Imaging Studies
- Ultrasound:
- Used to visualize the thyroid gland, assess nodules, and check for any structural abnormalities.
- Radioactive Iodine Uptake Test:
- Measures how much iodine the thyroid absorbs, helping differentiate between types of hyperthyroidism.
- CT or MRI:
- May be used in specific cases, particularly when evaluating large goiters or tumors.
Other Considerations
- Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA):
- If nodules are detected, this biopsy may be performed to check for cancerous cells.
The cost of thyroid disorder treatment in India:
Hypothyroidism Treatment
- Hormone Replacement Therapy:
- Levothyroxine (e.g., Thyronorm, Eltroxin): Typically costs between ₹100 to ₹500 per month, depending on the brand and dosage.
- Regular Monitoring:
- TSH Blood Tests: Each test usually costs between ₹300 to ₹1,000. Patients typically require these tests every 6 to 12 months.
Hyperthyroidism Treatment
- Antithyroid Medications:
- Methimazole or Carbimazole: Costs can range from ₹500 to ₹1,500 per month, depending on the dosage and brand.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy:
- This treatment generally costs between ₹30,000 to ₹60,000 for a single session, depending on the facility.
- Surgery:
- A thyroidectomy can cost anywhere from ₹50,000 to ₹1,50,000 or more, depending on the complexity of the surgery and the hospital.
Additional Costs
- Consultation Fees: Visiting an endocrinologist or general physician can range from ₹500 to ₹2,000 per visit.
- Imaging Studies:
- Ultrasound can cost around ₹1,000 to ₹3,000.
- A radioactive iodine uptake test may cost around ₹3,000 to ₹5,000.
